Predictive Modeling Terms:

Censoring is a common issue in survival analysis because it is often impossible to observe the exact time to event for all subjects. For example, in a study of cancer patients, some patients may be lost to follow-up before the end of the study period, and their time to death (or other event of interest) is unknown.
Censoring can be classified into three types:
- Right-censoring: This is the most common type of censoring in survival analysis. Right-censoring occurs when the event of interest has not occurred for some subjects at the end of the study period. For example, if a study follows patients for five years and some patients are still alive at the end of the study, their time to death is right-censored.
- Left-censoring: This occurs when the event of interest has already occurred for some subjects before they enter the study. For example, if a study examines the time to HIV diagnosis, subjects who are already diagnosed with HIV before the study begins are left-censored.
- Interval-censoring: This occurs when the exact time to the event of interest is not known, but it is known to have occurred within a certain interval. For example, if a study follows patients for regular check-ups and a patient’s cancer is detected during one of the check-ups, but the exact time of cancer onset is unknown, the time to cancer onset is interval-censored.
Censoring is an important issue to consider in survival analysis because it can bias the estimates of the survival function and other related statistics if not handled properly. Special statistical methods, such as the Kaplan-Meier estimator or the Cox proportional hazards model, have been developed to account for censoring in survival analysis.
The cumulative hazard rate (sum of h(t) from t = 0 to t = t) represents accumulated risk over time.
Spline variables are often used to capture the effects of nonlinear relationships in financial models. For example, if the relationship between a company’s revenue and its advertising spend is not linear, spline variables can be used to model the relationship accurately.
Spline variables can also be used to address issues such as multicollinearity and overfitting in regression analysis. By using spline variables, the modeler can fit a curve that captures the underlying relationship between the variables without introducing unnecessary complexity into the model.
Spline variables are a useful tool in financial modeling for capturing nonlinear relationships between variables and improving the accuracy and robustness of the model.
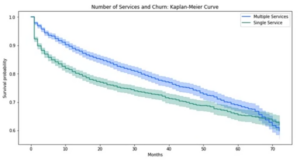
Survival Analysis allows us to consider cases with incomplete or censored data.
The Survival Function is defined as S(t)=P(T>t). It measures the probability that a subject will survive past time t.
This function:
- Is decreasing (non-increasing) over time
- Starts at 1 for all observations when t=0
- Ends at 0 for a high-enough t
Common survival models include:
- Cox Proportional Hazard (CPH) model: Assumes features have a constant proportional impact on the hazard rate.
- Accelerated Failure Time (AFT) models (several variants including the Weibull AFT model)
- Black-Scholes Model: This method is used to value a financial asset portfolio using option pricing theory, taking into account the volatility of the portfolio’s cash flows.
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model: This method calculates the present value of future cash flows generated by an asset portfolio using a discount rate that reflects the risk of the portfolio.
- Comparable Transactions: This method compares the subject financial asset portfolio to similar portfolios that have been recently sold in the market.
- Mark-to-Market: This technique compares the value of the financial asset portfolio to the current market value of similar assets.
- Mark-to-Model: This method uses a proprietary model to value the financial asset portfolio, taking into account factors such as credit risk and cash flow.
- Monte Carlo Simulation: This method uses computer simulations to model the potential performance of the financial asset portfolio under different economic scenarios.
- Risk-Adjusted Return on Capital (RAROC) Model: This technique calculates the return on capital of the financial asset portfolio adjusted for risk.
- Statistical Modeling: This technique uses historical data to predict future performance of the financial asset portfolio. It can include factors such as credit score, loan-to-value ratio, and geographic location.

